What is ISO 27001? Your Ultimate Guide to Information Security

Information is one of an organisation’s most valuable assets. As cyber threats grow in frequency and complexity, the need to protect data through structured, internationally recognised frameworks has never been greater.
If you’re wondering what ISO 27001 is, this guide will help you understand its purpose, scope, benefits, and implementation process.
What Is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is the international standard for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Published by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), it provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Organisations pursue ISO 27001 certification to:
- Demonstrate commitment to managing information security risks.
- Comply with legal and regulatory obligations.
- Strengthen internal security practices and external trust.
Why Should You Care About ISO 27001?
An organization that achieves certification to ISO 27001 has demonstrated that it takes information security seriously. By implementing an ISMS, an organization exhibits its commitment to protecting its data and the data of its customers, employees, and other stakeholders.
Organizations that are certified to ISO 27001 can use the certification to show their compliance with GDPR, PCI DSS, and other important regulations. In some cases, certification to ISO 27001 may even be a requirement for doing business with certain customers or partners.
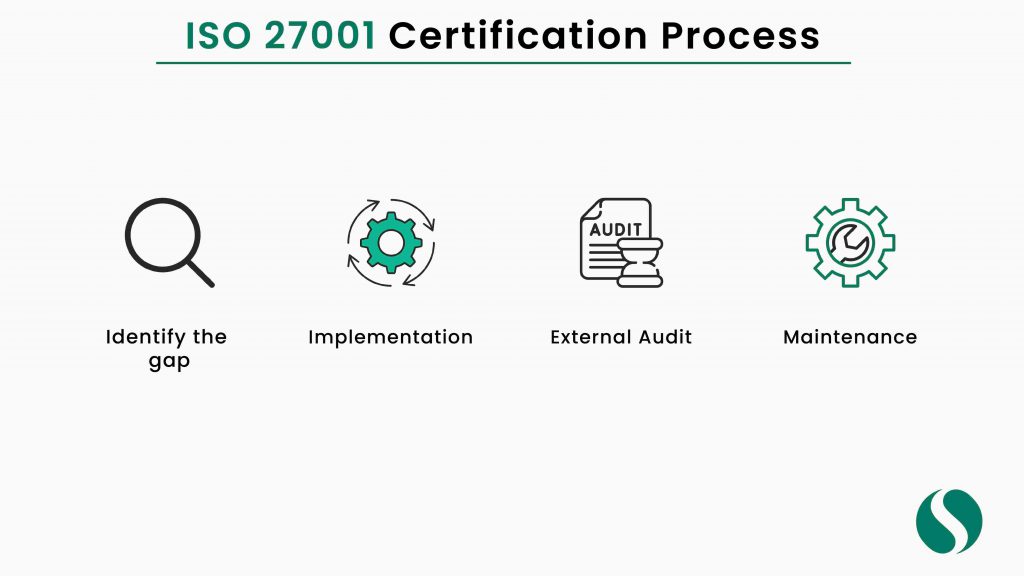
How Do You Become Certified?
The first step is to undertake a gap analysis to establish where your organization’s ISMS currently falls short of the requirements outlined in ISO 27001. Once you’ve identified the gaps, you can commence working on closing them. This usually involves implementing new processes and controls, and training employees on how to use them properly.
Once your gap analysis is complete and your ISMS is up to par, you’ll need to undergo an audit from a certifying body. The auditors will verify that your ISMS meets all the requirements of ISO 27001. If everything checks out, you will have achieved ISO 27001 Certification!
Key Domains of ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 standard covers several critical domains that support the framework of a robust ISMS:
- Risk Assessment and Treatment: Identify, evaluate, and mitigate information security risks.
- Security Policies: Define high-level management direction and support.
- Asset Management: Ensure information assets are identified, classified, and protected.
- Access Control: Limit access to information based on business and security needs.
- Cryptography: Use encryption to protect data confidentiality and integrity.
- Physical and Environmental Security: Safeguard physical infrastructure from unauthorised access or environmental damage.
- Operations Security: Establish secure operations, including monitoring and change management.
- Incident Response: Define responsibilities and actions in the event of a security breach.
Each domain reinforces ISO 27001’s goal of systematic and continual risk management.
ISO 27001 and Security Practices
Implementing ISO 27001 strengthens an organisation’s overall security posture. It:
- Formalises information security policies and procedures.
- Promotes a culture of security awareness among staff.
- Reduces risk of breaches through documented preventative controls.
- Enhances response to incidents and minimises damage.
ISO 27001 helps organisations protect client data, intellectual property, and reputation while enabling secure business continuity.
Compliance Requirements for ISO 27001
To achieve and maintain ISO 27001 compliance, organisations must meet several core requirements:
- Documentation: Develop required policies, risk registers, and statements of applicability.
- Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal assessments to ensure ISMS compliance.
- Management Review: Senior management must review ISMS performance periodically.
- Corrective Actions: Address non-conformities through formal improvement processes.
- Continual Improvement: Update and optimize controls and documentation as threats evolve.
Compliance is an ongoing cycle, not a one-time project.
Preparing for ISO 27001 Certification
Preparation is key to achieving ISO 27001 certification efficiently:
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Assess current practices against ISO 27001 requirements.
- Define the Scope: Clearly outline the areas, departments, or systems your ISMS will cover.
- Implement Controls: Apply appropriate controls from Annexe A of the standard.
- Develop ISMS Documentation: Create policies, procedures, and risk treatment plans.
- Train Your Team: Ensure staff understand their responsibilities.
- Perform Internal Audits: Validate your ISMS before the certification audit.
A risk-based approach ensures resources focus on areas of greatest vulnerability.
ISO 27001 Consultancy and Documentation Toolkit
For many organisations, expert support can simplify the certification journey. Engaging a consultant can provide direction and help fast-track implementation.
A documentation toolkit also ensures the necessary materials are available and aligned with ISO requirements.
Many organisations engage consultants to:
- Assist with gap analysis and risk assessments.
- Tailor the ISMS documentation to suit their business.
- Prepare for the certification audit.
A documentation toolkit typically includes:
- Pre-formatted policy templates.
- Risk assessment and treatment worksheets.
- Internal audit and corrective action forms.
These tools accelerate the certification process and ensure documentation meets ISO expectations.
ISO/IEC 27001 Training and Certification
Professional ISO 27001 training supports those managing or auditing an ISMS. Training types include:
- Foundation Courses: Introduce ISO 27001 principles and structure.
- Internal Auditor Training: Teaches how to assess ISMS effectiveness internally.
- Lead Auditor Certification: For professionals conducting third-party audits.
- Implementation Training: Guides participants through building and managing an ISMS.
Accredited training ensures your team is equipped to maintain compliance confidently.
Benefits of Identifying Information Security Risks
A key strength of ISO 27001 is its proactive approach to risk management. Identifying and addressing risks early helps:
- Prevent security breaches before they occur.
- Allocate resources more efficiently.
- Strengthen incident response planning.
- Align information security with business objectives.
This approach creates a culture of accountability and resilience.
2022 Update: Annexe A Controls Restructuring
The 2022 revision of ISO 27001 restructured Annexe A from 114 controls across 14 categories to 93 controls grouped under 4 control themes:
- Organisational Controls
- People Controls
- Physical Controls
- Technological Controls
This change aligns the framework with modern security needs and simplifies control mapping for implementers. Organisations should review and update their existing ISMS documentation and control mappings to reflect these changes.
Why ISO 27001 Still Matters
As threats to data and information systems evolve, ISO 27001 remains a trusted, comprehensive standard for protecting organisational assets.
Its structure supports continuous improvement, ensures regulatory compliance, and reinforces stakeholder confidence.
By aligning your information security with ISO 27001, your organisation demonstrates leadership in managing risk and safeguarding business operations.
FAQ
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for establishing a risk-based Information Security Management System (ISMS). It helps organisations protect data and meet legal, regulatory, and customer requirements.
What are the key ISO 27001 requirements?
Key requirements include documented policies, a risk assessment framework, internal audits, management reviews, and continuous improvement practices.
Is ISO 27001 certification mandatory?
ISO 27001 certification is not mandatory, but it is strongly recommended for organisations managing sensitive information or operating in regulated industries.
How long does ISO 27001 certification take?
The process typically takes 3 to 12 months, depending on the organisation’s size, complexity, and existing security maturity.
What are the benefits of ISO 27001 certification?
Benefits include improved information security, stronger compliance, enhanced trust with stakeholders, and a competitive edge.
How is ISO 27001 different from ISO 27002?
ISO 27001 outlines the requirements for an ISMS, while ISO 27002 guides the implementation of its controls.
